Recommended Growth Factors for Culturing Different Organoids

Organoids are defined as 3D structures grown from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), adult stem cells (stem cells extracted from specific tissues), and organ-specific cell clusters derived from human tissue cells. Organoids self-organize through cell sorting to mimic the complex structures and basic functional properties of various specific organs or tissues.
Organoids are miniature versions of human organs, similar in structure and physiology to actual organs. Human organoids have been successfully generated for a wide range of organs, including the intestine, lung, thyroid, stomach, heart, kidney, liver, brain, and retina. These mini-organs can be stored in biobanks for basic research, such as disease modeling and developmental biology, but they can also be used for translational research, such as drug screening. Furthermore, the potential clinical applications of organoids are diverse, including personalized and regenerative medicine.
Recommended growth factors for culturing different organoids
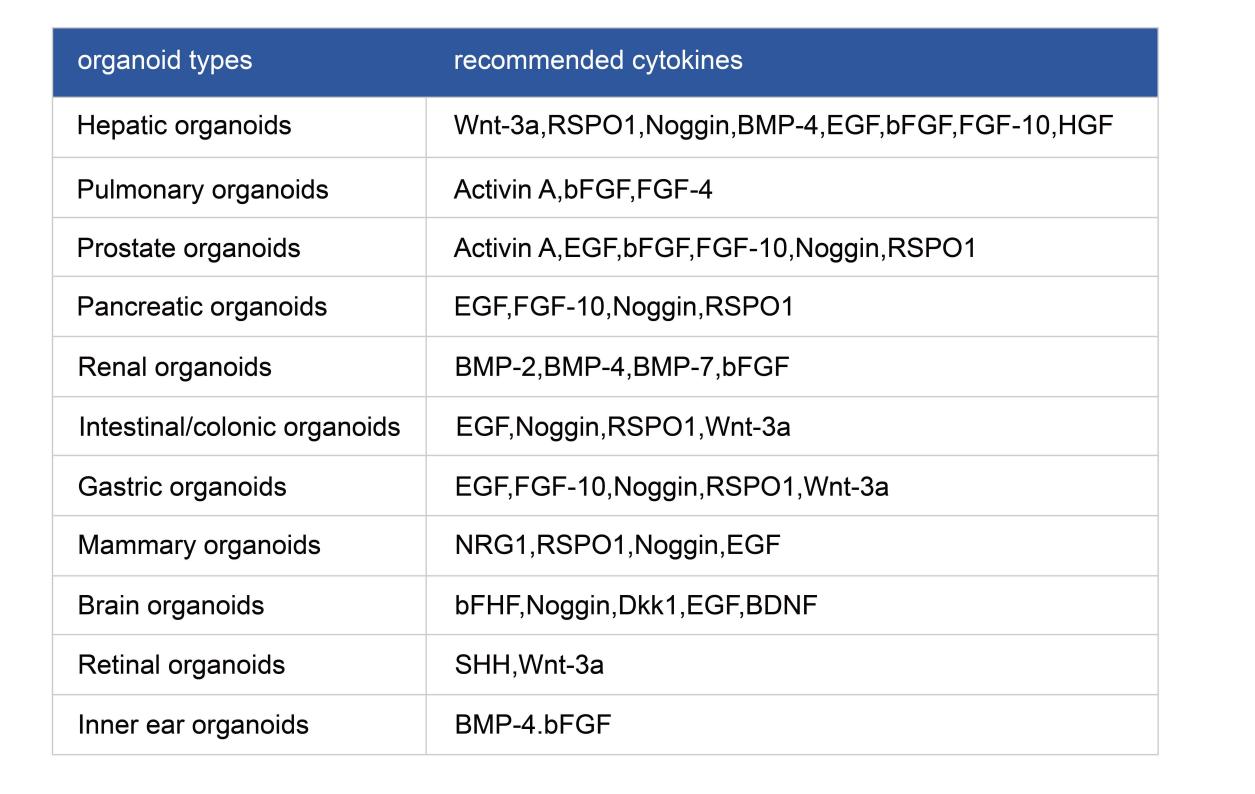
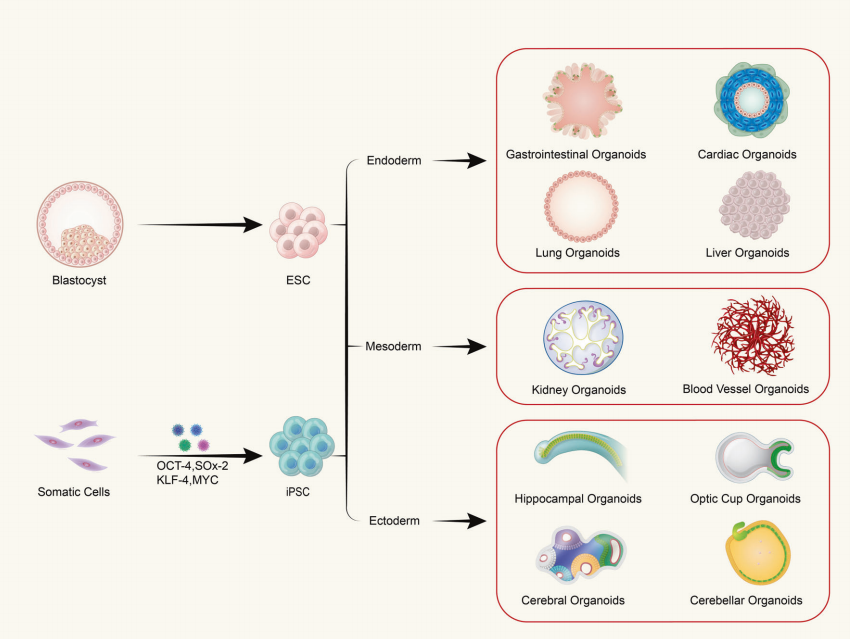
Figure: Schematic Diagram of Various Organs Derivable from Pluripotent Stem Cells.
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are used in research. Somatic cells can be reprogrammed into iPSCs by introducing four transcription factors. As development progresses, the blastocyst differentiates into embryonic stem cells, which further form all three embryonic germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. The embryonic endoderm subsequently gives rise to the gastrointestinal system, heart, lungs, and liver. The mesoderm develops into the kidneys and vascular system, while the ectoderm forms the neural ectoderm. Eventually, the brain develops with different regions, including the hippocampus, optic cup, and cerebellum. 3D organoid technology can reproduce all the structural and functional features mentioned above in vitro.
Commonly Used Growth Factors in Organoid Research
Wnt -3a
Alternative Names:Wingless-type MMTV Integration Site Family, Member 3a
Function: Wnt3a, a member of the Wnt family, plays a crucial role in regulating various cellular processes, including self-renewal, proliferation, differentiation, and motility. Wnts can bind to cell membrane receptors and play key roles in autocrine regulation and/or participate in paracrine modulation by binding to neighboring cell membrane receptors. The signaling pathway mediated by Wnt genes is called the Wnt signaling pathway. Wnt3a promotes or inhibits tumor progression through the canonical Wnt signaling pathway, depending on the type of cancer. Additionally, the activity of the Wnt3a signaling pathway can be inhibited by various proteins or chemicals. During embryonic development, Wnt-3a is necessary for the normal development of the hippocampus, the formation of anterior-posterior patterns, the development of somatic cells, and the formation of tail buds. Wnt-3a also promotes self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells, neural stem cells, and embryonic stem cells.
RSPO1
Alternative Names:R-Spondin 1 ;Roof Plate-specific Spondin 1
Function: R-Spondin 1 (RSPO1, Roof plate-specific Spondin 1) is a secreted protein with a molecular weight of 27 kDa, sharing approximately 40% sequence homology with the other three members of the R-Spondin family. Injection of recombinant RSPO1 in mice leads to activation of β-catenin and proliferation of intestinal crypt epithelial cells, improving experimental colitis. As the field of organoids expands, research on RSPO1 as a supplement in cell culture is also increasing. RSPO1 is widely used in the workflow of organoid cell culture and is an important component for promoting the growth and survival of three-dimensional organoids.
Noggin
Alternative Names:NOG, SYM1, symphalangism 1 (proximal), synostoses (multiple) syndrome 1, SYNS1, SYNS1A
Functions: Noggin can inhibit the TGF-β family ligands by preventing them from binding to their respective receptors. Initially discovered as an antagonist of BMP-4, Noggin has been shown to modulate the activity of other BMPs (BMP-2, 7, 13, and 14). Noggin is highly conserved in vertebrates. Secreted Noggin protein regulates the activity of bone morphogenetic proteins during development. The role of the BMP signaling antagonist Noggin in the development of osteolytic bone metastasis in prostate cancer. The lack of expression of the BMP antagonist Noggin in osteoblastic, cancer-derived cell lines is a determinant factor for the osteoblastic response induced by their bone metastases. Conversely, osteolytic, cancer-derived cell lines constitutively express Noggin.
EGF
Alternative Names:Urogastrone, URG
Functions: Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a small growth factor containing 53 amino acid residues that can stimulate the proliferation of mesenchymal and epithelial cells. The mature protein is much smaller, consisting of only 53 amino acids, and is generated by proteolytic cleavage of the EGF domain near the transmembrane region. EGF, along with Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF-2), induces the proliferation of neural precursor cells isolated from specific regions of the embryonic and adult brain. The biological activities of EGF include epithelial development, angiogenesis, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, fibroblast proliferation, and colony formation of epithelial cells in culture.
bFGF
Alternative Names:bFGF, FGF basic, FGF2, FGF-2, fibroblast growth factor 2 (basic), HBGF-2, Prostatropin
Functions: bFGF, a member of the FGF superfamily, is a highly specific chemotactic and mitogenic factor for many cell types and appears to be involved in tissue remodeling of damaged tissues such as ulcer healing, vascular repair, and traumatic brain injury. bFGF is an important component of human embryonic stem cell culture medium. Additionally, bFGF protein is a heparin-binding cationic protein involved in various pathological conditions, including angiogenesis and the growth of solid tumors. Therefore, bFGF is considered a target for cancer chemoprevention and treatment strategies. bFGF is commonly used as a key component in cell culture media, such as human embryonic stem cell culture medium and serum-free culture systems.
Related Product
|
Product Name |
Catalog Number |
|
Recombinant Human Wnt -3a protein |
C230259 |
|
Recombinant Human RSPO1 Protein |
C230254 |
|
Recombinant Human Noggin Protein |
C230462 |
|
Recombinant Human EGF Protein |
C230328 |
|
Recombinant Human bFGF/FGF-2 Protein |
C230295 |
|
Recombinant Human FGF-4 Protein |
C230346 |
|
Recombinant Human FGF-10 Protein |
C230418 |
|
Recombinant Human/Mouse/Rat BMP-2 Protein |
C230308 |
|
Recombinant Human BMP-4 Protein |
C230310 |
|
Recombinant Human BMP-7 Protein |
C230311 |
|
Recombinant Human HGF Protein |
C230260 |
|
Recombinant Human NRG1-beta1 Protein |
C230454 |
|
Recombinant Human/Mouse/Rat Activin A Protein |
C230520 |
|
Recombinant Human BDNF Protein, His Tag |
C230262 |
|
Recombinant Human DKK-1 Protein |
C230321 |
|
Recombinant Human Sonic Hedgehog N-Terminus (Human SHH) |
C230493 |
